The band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, often featured in the New York Times, is a crucial part of how our bodies move. This band, known as a tendon, helps your muscles pull on your bones so you can walk, run, and play. Without these strong bands, you wouldn’t be able to move around easily!
Understanding the band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, as highlighted in the New York Times, is important for keeping your body healthy. Tendons are made of tough, stretchy fibers that allow your muscles to move your bones. Taking care of these tendons helps you avoid injuries and stay active.
What is the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT?
The band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, as detailed in the New York Times, is referred to as a tendon. Tendons are strong, flexible fibers that act as vital links between muscles and bones, allowing for movement. When muscles contract, they pull on these tendons, which then move the bones, enabling actions like walking, running, and lifting. Understanding tendons’ role in our body is crucial for appreciating how we move and function daily.
Why the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT is Important
The band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, highlighted by the New York Times, is essential for all physical activities. Tendons are responsible for transmitting the force generated by muscles to bones, making movement possible. Without tendons, even simple actions like standing up or holding objects would be challenging. Maintaining tendon health is critical for preventing injuries and ensuring that our body remains agile and strong throughout life.
How the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT Helps Us Move
Tendons, the band of tissue connecting muscle and bone as featured in the New York Times, play a crucial role in facilitating movement. They act as bridges that link muscles to bones, allowing for smooth and coordinated actions. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the tendon, which then moves the bone in the desired direction. This process is fundamental to every movement we make, from simple gestures to complex athletic activities.
The Anatomy of the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT
The anatomy of the band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, often discussed in the New York Times, reveals its intricate design. Tendons are composed of tightly packed collagen fibers, which provide both strength and flexibility. These fibers are arranged in a parallel fashion, allowing tendons to withstand the stress and strain of daily activities. Understanding this anatomy helps us appreciate how tendons function and why they are so crucial to our movement.
Collagen Fibers: The Building Blocks
Collagen fibers are the building blocks of tendons, providing the strength and elasticity needed for movement. These fibers are made of proteins that are tightly woven together, giving tendons their characteristic toughness. Collagen is essential for the durability of tendons, enabling them to handle the repeated stresses of physical activity without breaking down.
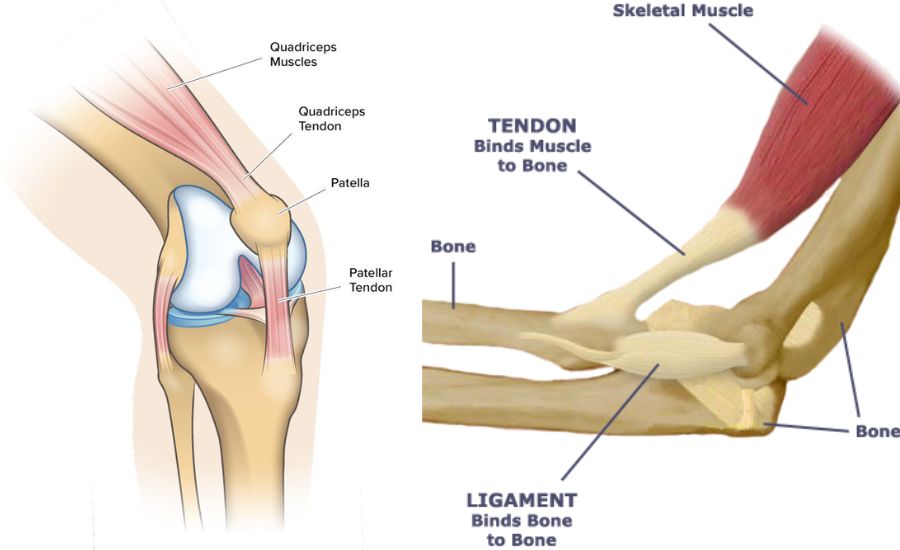
How Tendons Connect Muscle to Bone
Tendons connect muscle to bone through a specialized structure that allows for efficient force transmission. At the muscle end, tendons blend with muscle fibers, while at the bone end, they integrate into the bone’s outer layer. This connection ensures that when muscles contract, the force is effectively transferred to the bone, resulting in movement.
Common Problems with the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT
The band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, as reported in the New York Times, can suffer from various issues that impact movement and overall health. Tendonitis, inflammation of the tendon, and tendon tears are common problems that can cause pain and limit mobility. These issues often result from overuse, injury, or inadequate tendon care.
Tendonitis: Causes and Symptoms
Tendonitis is a common problem where tendons become inflamed, leading to pain and swelling. Causes include repetitive motions, overuse during exercise, and lack of proper warm-up. Symptoms typically involve localized pain, tenderness, and difficulty moving the affected area. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further complications.
Tendon Tears: Understanding the Risks
Tendon tears occur when the fibers within the tendon are stretched beyond their capacity, leading to a partial or complete tear. This injury can result from sudden, forceful movements or chronic overuse. The risks are higher in individuals who engage in high-impact sports without proper conditioning. Tendon tears often require medical intervention and can significantly affect one’s ability to perform daily activities.
How to Keep Your Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT Healthy
Keeping the band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, as recommended by the New York Times, healthy is crucial for maintaining an active lifestyle. Proper care, including regular stretching, strengthening exercises, and adequate rest, can help maintain tendon health and prevent injuries.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Stretching exercises help maintain tendon flexibility, reducing the risk of injuries. Regular stretching can keep tendons pliable and able to handle the demands of physical activity. Strengthening exercises, on the other hand, build muscle support around the tendons, reducing the load on them during movement and further preventing injuries.
The Importance of Warming Up
Warming up before physical activity is essential for preparing tendons for the stress of exercise. A proper warm-up increases blood flow to the muscles and tendons, making them more elastic and less prone to injury. Skipping this step can lead to tendon strains or tears, especially during intense activities.
The Role of Tendons in Your Body According to the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT
Tendons play a pivotal role in body movement by connecting muscles to bones, as discussed in the New York Times. They ensure that the force generated by muscle contractions is efficiently transferred to bones, enabling smooth and coordinated movements. Without tendons, our ability to move would be severely impaired, highlighting their importance in our daily lives.
How Injuries Affect the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT
Injuries to the band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, as covered in the New York Times, can have a significant impact on movement and overall health. Tendon injuries, such as tendonitis and tears, can cause pain, swelling, and limited mobility, affecting daily activities and quality of life.
Tendonitis and Its Impact
Tendonitis can lead to chronic pain and discomfort, making it difficult to perform even simple tasks. The inflammation can cause stiffness and reduce the range of motion, impacting overall mobility. If left untreated, tendonitis can lead to more severe tendon damage, requiring prolonged treatment and recovery.
Dealing with Tendon Tears
Tendon tears are serious injuries that often require medical intervention, such as surgery or physical therapy. A torn tendon can result in significant pain and loss of function, making it challenging to carry out routine activities. Proper rehabilitation is crucial for regaining strength and mobility after a tendon tear.
Tips for Preventing Tendon Injuries
Preventing tendon injuries is key to maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle. The New York Times offers valuable insights into strategies for protecting these vital tissues, including proper warm-up, avoiding overuse, and incorporating flexibility and strength training into your routine.
Warming Up: A Key to Prevention
A thorough warm-up is essential for preparing tendons for the demands of physical activity. It increases elasticity and reduces the risk of strains and tears. A proper warm-up should include dynamic stretching and low-intensity exercises that gradually increase in intensity.
Avoiding Overuse: Give Your Tendons a Break
Overuse is a common cause of tendon injuries. It’s important to allow tendons time to recover between workouts, especially after intense physical activity. Incorporating rest days and varying your exercise routine can help prevent overuse injuries and keep your tendons healthy.
The Best Exercises for the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT
The New York Times highlights several exercises that are beneficial for maintaining the health of the band of tissue connecting muscle and bone. These exercises focus on stretching, strengthening, and improving balance, all of which contribute to tendon health.
Stretching Exercises: Keeping Tendons Flexible
Regular stretching exercises, such as calf and hamstring stretches, are essential for keeping tendons flexible and reducing the risk of injury. Stretching should be done gently and consistently, especially after exercise when tendons are warm and more pliable.
Strengthening Exercises: Building Muscle Support
Strengthening exercises, like resistance training, help build muscle around the tendons, providing additional support and reducing the risk of strain. These exercises should be performed with proper form and gradually increased in intensity to avoid injury.
Balance Exercises: Improving Coordination
Balance exercises, such as yoga or balance board activities, improve coordination and reduce the likelihood of tendon injuries by enhancing the stability of joints. These exercises can be integrated into your regular workout routine to help protect tendons and maintain overall musculoskeletal health.
Recommended for you: Coffemanga: The Exciting Blend of Coffee and Manga Magic
Understanding Tendon Repair: What the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT Tells Us
Understanding tendon repair, as discussed in the New York Times, is crucial for recovery from injuries. Tendon repair can involve various treatments, including physical therapy, medication, and surgery, depending on the severity of the injury. Proper tendon repair is essential for restoring function and preventing future injuries.
Physical Therapy: Strengthening and Flexibility
Physical therapy is a common treatment for tendon injuries, focusing on exercises that strengthen the tendon and improve flexibility. These exercises help restore normal movement and prevent future injuries by addressing the underlying causes of tendon damage.
Medication and Surgery: Advanced Treatment Options
In more severe cases, tendon injuries may require medication to reduce inflammation or surgery to repair torn fibers. Surgery is usually reserved for serious tears that cannot heal on their own. Post-surgery rehabilitation is crucial for regaining full function and strength in the affected tendon.
How to Treat Tendon Injuries: Advice from the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT
Treating tendon injuries effectively is crucial for a full recovery. The New York Times provides valuable advice on managing these injuries, including rest, ice, and appropriate medical care.
Rest and Recovery: Essential for Healing
Rest is one of the most important aspects of tendon injury treatment. Allowing the affected tendon time to heal helps prevent further damage and ensures a more complete recovery. During rest, it’s important to avoid activities that strain the tendon.
Using Ice and Pain Medications
Applying ice to the injured tendon can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Over-the-counter pain medications, like ibuprofen, can also be used to manage discomfort and inflammation. These treatments should be used as part of a comprehensive recovery plan.
The Connection Between Tendons and Overall Health
Tendons play a vital role in overall health by enabling movement and supporting daily activities. Healthy tendons contribute to a well-functioning musculoskeletal system, allowing you to stay active and maintain physical fitness. Conversely, tendon injuries can lead to decreased mobility and a lower quality of life.
Future Research on the Band of Tissue Connecting Muscle and Bone NYT
Future research on the band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, as explored by the New York Times, promises to yield exciting advancements in tendon health. Scientists are continually studying new techniques and technologies to improve tendon healing and understand how tendons change with age.
Enhancing Tendon Healing: New Techniques
One area of research focuses on enhancing tendon healing through advanced techniques like regenerative medicine and imaging technologies. These innovations could lead to faster recovery times and more effective treatments for tendon injuries.
Aging and Tendons: What Researchers Are Finding
Another key area of research is understanding how tendons age and what can be done to maintain their health over time. As we age, tendons can become less elastic and more prone to injury. Research in this area aims to find ways to keep tendons strong and flexible throughout life.
Conclusion
Understanding the band of tissue connecting muscle and bone, called tendons, is very important for staying healthy and active. Tendons help our muscles move our bones so we can walk, run, and play. Taking care of these strong bands with simple things like stretching and warming up can keep us moving without pain.
As we learn more about tendons, we can find even better ways to keep them strong and healthy. Whether you’re playing sports or just enjoying everyday activities, healthy tendons are key to having fun and staying fit. Remember, taking care of your tendons today means more fun tomorrow!
FAQs
Q: What is the band of tissue connecting muscle and bone?
A: The band of tissue connecting muscle and bone is called a tendon. Tendons help your muscles move your bones so you can walk, run, and play.
Q: Why are tendons important?
A: Tendons are important because they allow your body to move. Without them, you wouldn’t be able to do everyday activities like walking or lifting things.
Q: How can I keep my tendons healthy?
A: You can keep your tendons healthy by stretching, doing strengthening exercises, and warming up before physical activity. It’s also important to rest and not overuse them.
Q: What happens if a tendon gets injured?
A: If a tendon gets injured, it can cause pain and make it hard to move. Rest and proper treatment are needed to help the tendon heal.
Q: What are researchers studying about tendons?
A: Researchers are studying new ways to help tendons heal faster and stay strong as we age. This could lead to better treatments for tendon injuries.
Explore More: Delicious Mielado: A Sweet Treat That Delights






